In our increasingly interconnected digital economy, data has become a valuable asset. Yet despite its immense value, the true potential of data often remains untapped due to fragmentation across isolated repositories, or data silos. These silos not only limit accessibility but also hinder innovation, collaboration, and efficient decision-making. Recognizing this critical barrier, ENACT is pioneering a transition from independent data stores towards unified, interoperable data ecosystems that can unlock data’s full potential across the edge-cloud continuum.
Today’s data storage practices typically involve isolated environments, each optimized individually but disconnected from others. Organizations struggle to access and share data efficiently due to varying standards, incompatible formats, and inflexible infrastructures. The consequences of these fragmented practices are tangible: duplicated efforts, slower innovation cycles, higher operational costs, and limited scalability. Addressing this, ENACT delivers a distributed Data & Object Space, significantly enhancing interoperability, security, and dynamic data sharing. The ENACT CCC Data Space is used for storing historical telemetry data and pilot-generated metadata in a distributed manner. In addition, ENACT CCC Data Space also extends the conventional concept of Data Spaces to allow for the sharing of code objects, such as executable scripts, that can be retrieved during application development. This constitutes a key ENACT innovation that promotes the collaboration and sharing among developers, thus enabling objects’ re-usability and accelerating application development.
ENACT’s vision for distributed storage and data spaces is inspired by emerging standards such as the International Data Spaces Association Reference Architecture Model (IDSA RAM) and GAIA-X; two leading initiatives in this regard. By aligning with these standards, ENACT ensures compatibility and future-proofing, while going significantly beyond their foundational principles. The project provides not just technical alignment but practical solutions to overcome current challenges in data discoverability, secure sharing, and policy enforcement.
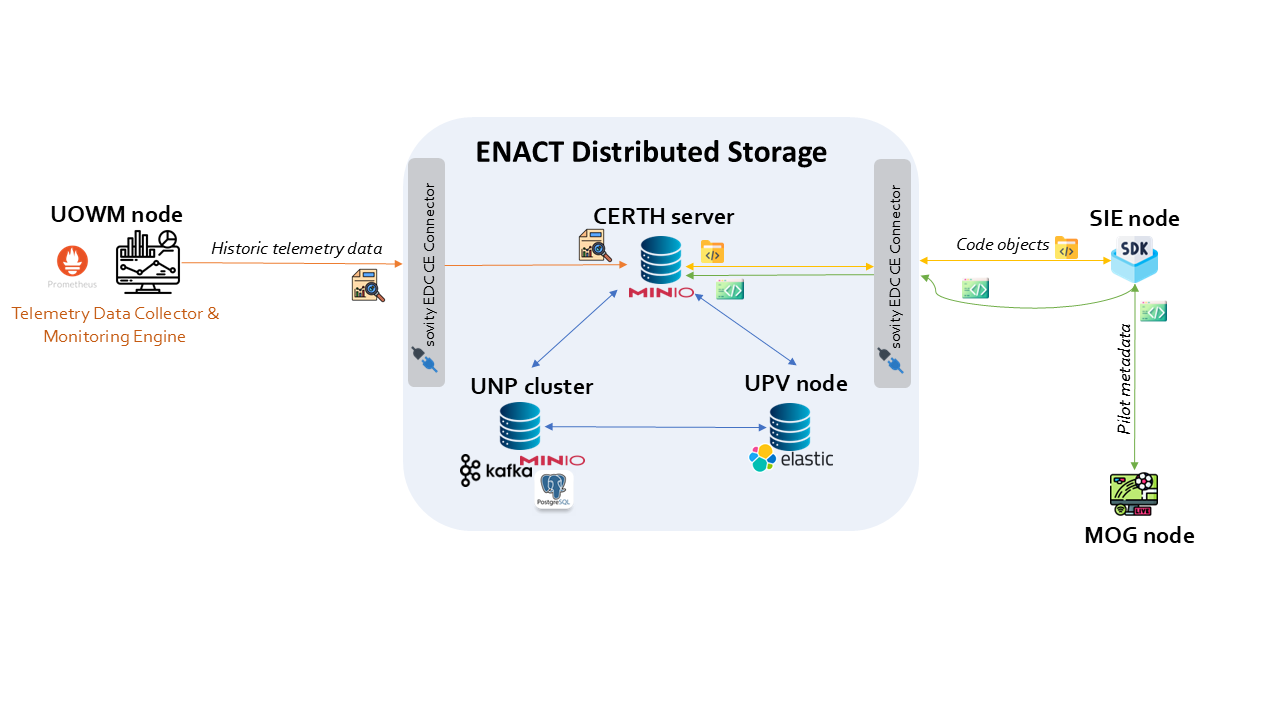
Data Space Architecture based on IDSA RAM
At the core of ENACT’s approach is the Data Manager component, designed to provide a robust, secure, and highly scalable solution for large-scale data storage and management across multiple storage points and computing nodes. Unlike traditional centralized storage models, ENACT’s Data Manager manages efficiently data assets distributed across the ENACT CCC, regardless of where and how they are stored, accessed, and processed. Through pertinent interoperability and retrieval mechanisms, it ensures data is always available where and when it’s needed, offering explicit advantages, such as data locality and reduced access times.
Access to the ENACT CCC Data Space is provided via the Data Access and Sharing Interfaces that are built upon the Sovity Dataspace Connector, an open-source connector that complies with the Data Space Connector concept and the standards introduced by IDSA and Gaia-X. Being aligned with such well-established standards, these interfaces facilitate seamless communication and interoperability among diverse systems and platforms. This design allows various entities to easily interact, share, and collaborate over data without concern for underlying technical differences.
To ensure robust security and compliance, ENACT integrates identity and access management policies through its Security & Access Control module. In particular, ENACT implements access control policies to ensure that each participant contributes and accesses data according to clearly defined rules and governance models based on the user’s identity and role and the usage rules defined per data asset. This ensures that data remains secure and accessible only to authorized parties.
Overall, by transitioning from isolated data silos to interoperable, distributed data stores, the ENACT CCC delivers an innovative Data & Object Space, offering various benefits including improved asset availability and content delivery times, controlled sharing of assets belonging to different owners while ensuring fine-grained access control and usage across multiple participants, as well as asset governance and sovereignty.